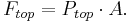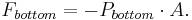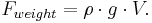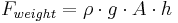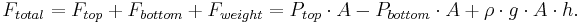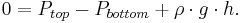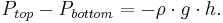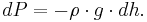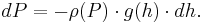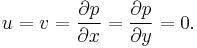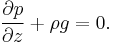Hydrostatic equilibrium
Hydrostatic equilibrium or hydrostatic balance occurs when compression due to gravity is balanced by a pressure gradient force in the opposite direction. For instance, the pressure gradient force prevents gravity from collapsing the Earth's atmosphere into a thin, dense shell, while gravity prevents the pressure gradient force from diffusing the atmosphere into space. Hydrostatic equilibrium is the current distinguishing criterion between dwarf planets and other small solar system bodies, and has other roles in astrophysics and planetary geology.
Contents |
Mathematical consideration
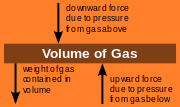
For a volume of a fluid which is not in motion or is in a state of constant motion, Newton's Laws state that it must have zero net force on it – the forces up must equal the forces down. This force balance is called the hydrostatic balance.
We can split the gas into a large number of cuboid volume elements. By considering just one element, we can work out what happens to the gas as a whole.
There are 3 forces: The force downwards onto the top of the cuboid from the pressure, P, of the fluid above it is, from the definition of pressure,
Similarly, the force on the volume element from the pressure of the fluid below pushing upwards is
In this equation, the minus sign comes from the direction – this force supports the volume element, rather than pulls it down (We are presuming that positive force acts down, if you read "down" as "up" the results are the same for equilibrium).
Finally, the weight of the volume element causes a force downwards. If the density is ρ, the volume is V and g the standard gravity, then:
The volume of this cuboid is equal to the area of the top or bottom, times the height - the formula for finding the volume of a cube.
By balancing these forces, the total force on the gas is
This is zero if the gas is not moving. If we divide by A,
Or,
Ptop − Pbottom is a change in pressure, and h is the height of the volume element – a change in the distance above the ground. By saying these changes are infinitesimally small, the equation can be written in differential form.
Density changes with pressure, and gravity changes with height, so the equation would be:
Note finally that this last equation can be derived by solving the three-dimensional Navier-Stokes equations for the equilibrium situation where
Then the only non-trivial equation is the  -equation, which now reads
-equation, which now reads
Thus, hydrostatic balance can be regarded as a particularly simple equilibrium solution of the Navier-Stokes equations.
Applications
Fluids
The hydrostatic equilibrium pertains to hydrostatics and the principles of equilibrium of fluids. A hydrostatic balance is a particular balance for weighing substances in water. Hydrostatic balance allows the discovery of their specific gravities.
Astrophysics
Hydrostatic equilibrium is the reason stars don't implode, or explode. In astrophysics, in any given layer of a star, there is a balance between the thermal pressure (outward) and the weight of the material above pressing downward (inward). This balance is called hydrostatic equilibrium. A star is like a balloon. In a balloon, the gas inside the balloon pushes outward and the atmospheric pressure plus the elastic material supply just enough inward compression to balance the gas pressure. In the case of a star, the star's internal gravity supplies the inward compression. The isotropic gravitational field compresses the star into the most compact shape possible: a sphere.
Note however that a star becomes a sphere only in the ideal case where only its own self-gravity is involved. In real situations there are other forces at play that alter the outcome, most notably centrifugal force from a star's rotation. A rotating star in hydrostatic equilibrium is an oblate spheroid up to a certain angular velocity; above that point it becomes a Jacobi (scalene) ellipsoid, and at still higher rotations piriform.[1] An extreme example of this is the star Vega, which has a rotation period of 12.5 hours and is about 20% fatter at the equator than at the poles because of it.
If the star has a massive nearby companion object then tidal forces come into play as well, distorting the star into an ellipsoidal shape when rotation alone would make it a spheroid. An example of this is Beta Lyrae.
It is also important for the intracluster medium, where it restricts the amount of gas that can be present in the core of a cluster of galaxies.
Planetary geology
The concept of hydrostatic equilibrium has also become important in determining whether an astronomical object is a planet, dwarf planet, or small solar system body. According to the definition of planet adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 2006, planets and dwarf planets are objects that have sufficient gravity to overcome their own rigidity and assume hydrostatic equilibrium. Sometimes this means a spheroid. However, in the cases of moons in synchronous orbit, tidal forces create a scalene ellipsoidal shape, and the quickly rotating dwarf planet Haumea also appears to be ellipsoidal.
Since the terrestrial planets and dwarf planets (and likewise the larger satellites, like the Moon and Io) have rough surfaces and so are not in perfect equilibrium, this definition evidently has some flexibility, but as of yet a specific means of quantifying an object's shape by this standard has not been announced. The amount of leeway afforded the definition could affect the classification of the asteroid Vesta, which appears to have solidified while in hydrostatic equilibrium but to have subsequently been significantly deformed by a large impact.[1]
Atmospherics
Hydrostatic equilibrium can explain why the Earth's atmosphere does not collapse to a very thin layer on the ground. In the atmosphere, the pressure of air decreases with increasing altitude. This causes an upward force, called the pressure gradient force, which tries to smooth over pressure differences. The force of gravity, on the other hand, almost exactly balances this out, keeping the atmosphere bound to the earth and maintaining pressure differences with altitude. Without the pressure gradient force, the atmosphere would collapse to a much thinner and denser shell around the earth, and without the force of gravity, the pressure gradient force would diffuse the atmosphere into space, leaving Earth with hardly any atmosphere.
See also
- List of Solar System objects in hydrostatic equilibrium
- Statics
- Two-balloon experiment
Notes
- ↑ Savage, Don; Jones, Tammy; and Villard, Ray (1995-04-19). "Asteroid or Mini-Planet? Hubble Maps the Ancient Surface of Vesta (Key Stages in the Evolution of the Asteroid Vesta)". Hubble Site News Release STScI-1995-20. http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/1995/20/image/c. Retrieved 2006-10-17.